Imagine this: your business is running smoothly, customers are happy, and everything seems to be on track. Then, out of nowhere, a disaster strikes—maybe it’s a cyberattack, a natural disaster, or even a simple hardware failure. Suddenly, your IT systems are down, and your entire operation is at a standstill. This is where an IT Disaster Recovery Plan comes into play.
An IT Disaster Recovery Plan is like your business’s safety net, ensuring that when things go wrong, you can get back on your feet quickly. It’s a crucial part of any business strategy, helping to minimize downtime, protect data, and keep your business running even when disaster strikes.
In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about IT Disaster Recovery Plans, from understanding what they are to developing one that works for your business. Whether you’re new to the concept or looking to refine your existing plan, this guide will give you the insights you need to protect your business from unexpected IT disasters.
Understanding IT Disaster Recovery Plan
At its core, an IT Disaster Recovery Plan (often abbreviated as DRP) is a documented, structured approach with instructions for responding to unplanned incidents that can affect IT systems. These incidents might include anything from a natural disaster like an earthquake to more common threats like cyberattacks or system failures.
The disaster recovery objectives are simple: to restore IT operations as quickly and efficiently as possible after a disruption. This means getting your servers back online, restoring lost data, and ensuring that your business can continue to operate with minimal interruption.
Why Is It Important?
In today’s digital world, your IT systems are the backbone of your business. Without them, you risk losing valuable data, customer trust, and revenue. An effective IT DRP (Disaster Recovery Plan) ensures that your business can recover quickly from any disaster, reducing downtime and minimizing losses.
Key Components of a Disaster Recovery Plan
Creating an IT Disaster Recovery Plan isn’t just about having a document ready in case something goes wrong. It involves careful planning, testing, and updating. Let’s explore the key elements of recovery plan that form a strong disaster recovery plan.
1. Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
Before you can develop a recovery plan, you need to understand the risks your business faces. This includes identifying potential disasters—both natural and man-made—that could impact your IT systems. A Business Impact Analysis (BIA) helps you assess the effects of these risks on your business operations.
Risk Assessment: Identify the risks to your IT infrastructure, such as hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
Business Impact Analysis: Determine the potential impact of these risks on your business operations, including the financial and operational consequences of downtime.
2. Recovery Objectives
Setting clear recovery objectives is crucial. These objectives guide your entire disaster recovery strategy.
Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This defines how quickly you need to restore your IT systems after a disaster. For example, if your RTO is 4 hours, your goal is to have your systems back online within that time frame.
Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This defines the maximum amount of data you can afford to lose, measured in time. For instance, an RPO of 1 hour means you should be able to recover all data up to an hour before the disaster.
3. Data Backup
Data is the lifeblood of any business, so protecting it is a top priority in any data disaster recovery plan. Regular backups ensure that you can restore lost data in case of an emergency.
Backup Strategy: Determine what data needs to be backed up, how often, and where the backups should be stored (on-site, off-site, or in the cloud).
Data Encryption: Ensure that your backup data is encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access.
4. Disaster Recovery Team
Your disaster recovery plan is only as good as the people responsible for executing it. A well-defined disaster recovery team ensures that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities during a disaster.
Team Roles: Assign specific roles to team members, such as IT administrators, communication leads, and business continuity planners.
Training and Drills: Regularly train your team and conduct disaster recovery drills to ensure everyone is prepared for a real-life scenario.
5. Communication Plan
Clear communication is essential during a disaster. Your communication plan should outline how information will be shared with employees, customers, and other stakeholders.
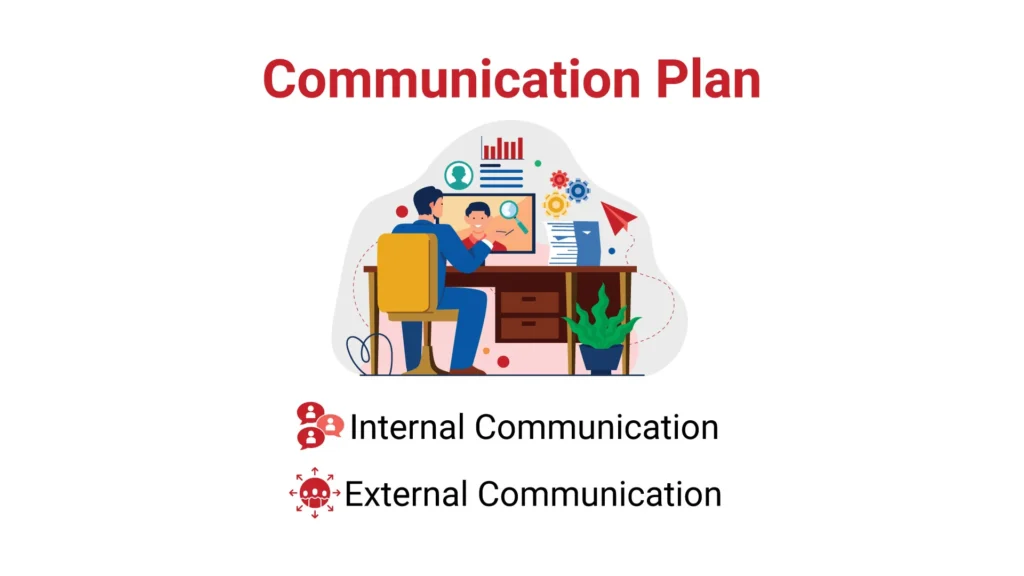
External Communication: Have a plan for keeping customers and partners informed about the status of your operations.
6. Testing and Maintenance
Your disaster recovery plan isn’t a one-and-done deal. It needs to be regularly tested and updated to ensure it remains effective.
Regular Testing: Conduct regular tests to ensure that your plan works as expected.
Plan Updates: Update your plan regularly to reflect changes in your IT infrastructure, business operations, or potential risks.
Developing an Effective Disaster Recovery Plan
Creating an IT Disaster Recovery Plan requires more than just understanding its components. You need a step-by-step approach to ensure that your plan is comprehensive and effective. Here’s how to develop a plan that will help you bounce back quickly from any disaster.
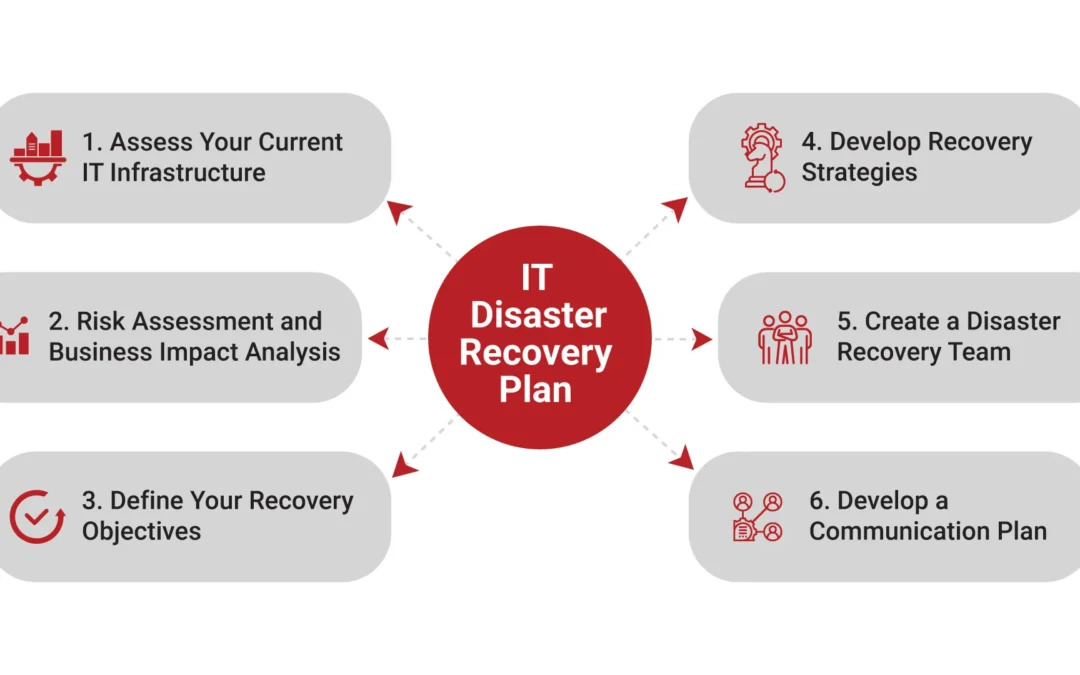
Step 1: Assess Your Current IT Infrastructure
Before you can develop a disaster recovery plan, you need to have a clear understanding of your current IT infrastructure. This includes identifying all hardware, software, and network components that are critical to your operations.
Inventory Your IT Assets: Make a detailed list of all your IT assets, including servers, workstations, network equipment, and software applications.
Identify Critical Systems: Determine which systems are essential for your business operations and would have the most significant impact if they were to fail.
Step 2: Conduct a Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis
As discussed earlier, a thorough risk assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA) are essential for developing an effective disaster recovery plan.
Identify Potential Risks: Consider all possible threats to your IT systems, including natural disasters, cyberattacks, and hardware failures.
Analyze the Impact: Determine how each risk could impact your business, including potential downtime, data loss, and financial implications.
Step 3: Define Your Recovery Objectives
Once you’ve assessed the risks, it’s time to set your recovery objectives. These will guide your entire disaster recovery strategy.
Set Your RTO and RPO: Clearly define your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) based on your business needs.
Align with Business Goals: Ensure that your recovery objectives align with your overall business goals and customer expectations.
Step 4: Develop Recovery Strategies
With your recovery objectives in place, you can start developing strategies to achieve them. This includes outlining specific IT disaster recovery procedures for different types of disasters.
Backup and Restore Procedures: Develop detailed procedures for backing up and restoring data. This should include instructions for regular backups and steps to follow in case of data loss.
System Recovery Procedures: Outline the steps needed to recover critical systems, including servers, databases, and network infrastructure.
Alternate Site Planning: Consider setting up an alternate site where your IT operations can continue in case your primary site is compromised.
Step 5: Create a Disaster Recovery Team
Assemble a team responsible for executing your disaster recovery plan. This team should include IT professionals as well as representatives from other business units.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities: Clearly define each team member’s role in the disaster recovery process.
Provide Training: Regularly train your team on the disaster recovery procedures and conduct drills to ensure they’re prepared for a real-life scenario.
Step 6: Develop a Communication Plan
Your communication plan should ensure that everyone involved in the disaster recovery process knows what to do and when.
Internal Communication: Establish clear lines of communication between your disaster recovery team members.
External Communication: Prepare templates for communicating with customers, partners, and the media in case of a disaster.
Step 7: Test and Maintain Your Plan
A disaster recovery plan is only effective if it’s kept up-to-date and regularly tested.
Regular Testing: Conduct regular disaster recovery drills to test your plan’s effectiveness and make necessary adjustments.
Ongoing Maintenance: Update your plan regularly to reflect changes in your IT infrastructure, business operations, or potential risks.
Best Practices for Disaster Recovery Planning
Creating an effective IT Disaster Recovery Plan is crucial, but following best practices can help you ensure that your plan is as robust and reliable as possible. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Involve All Stakeholders
Your disaster recovery plan should be a collaborative effort that involves all key stakeholders in your organization. This includes IT staff, business leaders, and even external partners.
Cross-Functional Collaboration: Involve representatives from different departments to ensure that all business functions are covered in the disaster recovery plan.
Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed about any updates or changes to the disaster recovery plan.
2. Prioritize Data Protection
Data is one of your most valuable assets, so protecting it should be a top priority in your disaster recovery plan.
Implement Robust Backup Solutions: Use reliable backup solutions that can store your data securely and ensure quick recovery.
Use Data Encryption: Encrypt your backup data to protect it from unauthorized access.
3. Keep It Simple
While your disaster recovery plan needs to be comprehensive, it should also be easy to understand and execute. Overly complex plans can be difficult to follow, especially during a crisis.
Simple and Clear Instructions: Ensure that your disaster recovery procedures are simple, clear, and easy to follow.
Avoid Technical Jargon: Use plain language that everyone can understand, avoiding unnecessary technical jargon.
4. Regularly Review and Update Your Plan
Your IT infrastructure and business needs are constantly evolving, so your disaster recovery plan should evolve too.
Annual Reviews: Review your disaster recovery plan at least once a year to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Update After Major Changes: Update your plan immediately after any significant changes to your IT infrastructure or business operations.
5. Test, Test, Test
Testing is one of the most critical aspects of disaster recovery planning. Without regular testing, you can’t be sure that your plan will work when you need it most.
Conduct Regular Drills: Run disaster recovery drills regularly to test your plan and identify any weaknesses.
Simulate Different Scenarios: Test your plan against different types of disasters to ensure it can handle a variety of situations.
Common Challenges in IT Disaster Recovery Plan
Despite careful planning, creating and executing an IT Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) can be challenging. Here are some common issues and ways to address them.
1. Limited Budget and Resources
Developing a comprehensive disaster recovery plan can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
Prioritize Critical Systems: Focus your resources on protecting the most critical systems and data.
Leverage Cloud Solutions: Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions can be more cost-effective than traditional on-premises options.
2. Scaling the Disaster Recovery Plan
As your business grows, your disaster recovery plan needs to scale with it. However, scaling can be challenging, especially if your plan is not designed with growth in mind.
Regularly Review and Update: Regularly update your disaster recovery plan to reflect changes in your business operations and IT infrastructure.
Consider Scalable Solutions: Use scalable disaster recovery solutions that can grow with your business.
3. Lack of Awareness and Training
A disaster recovery plan is only effective if everyone involved knows their role and how to execute the plan.
Regular Training: Conduct regular training sessions to ensure that all team members are familiar with the disaster recovery procedures.
Awareness Programs: Implement awareness programs to educate all employees about the importance of disaster recovery planning.
4. Keeping Up with Changing Technology
Technology is constantly evolving, and your disaster recovery plan needs to keep up with these changes.
Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest trends and technologies in disaster recovery to ensure your plan remains relevant.
Update Regularly: Regularly update your disaster recovery plan to incorporate new technologies and best practices.
Expert Tips for IT Disaster Recovery Plan
To ensure your IT Disaster Recovery Plan is as effective as possible, consider these expert tips:
1. Automate Where Possible
Automation can significantly improve the speed and reliability of your disaster recovery processes.
Automated Backups: Use automated backup solutions to ensure that your data is regularly and reliably backed up.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS): Consider using DRaaS solutions that automate much of the disaster recovery process, reducing the risk of human error.
2. Focus on Communication
Clear communication is critical during a disaster, so make sure your communication plan is robust and well-practiced.
Communication Tools: Use reliable communication tools that can operate even during an IT outage.
Regular Drills: Test your communication plan regularly to ensure it works effectively under pressure.
3. Consider Third-Party Assistance
If developing a disaster recovery plan seems overwhelming, consider working with a third-party expert.
Consulting Services: Many consulting firms specialize in disaster recovery planning and can help you develop a robust plan tailored to your needs.
Managed Services: Consider outsourcing your disaster recovery to a managed service provider who can handle everything from planning to execution.
4. Document Everything
Documentation is key to a successful disaster recovery plan. Make sure everything is documented and easily accessible.
Comprehensive Documentation: Document all disaster recovery procedures, roles, and responsibilities in detail.
Easy Access: Ensure that your disaster recovery documentation is easily accessible to all relevant team members.
To Wrap Up
An IT Disaster Recovery Plan is not just a technical document—it’s a vital part of your business strategy that can mean the difference between a minor disruption and a major catastrophe. By understanding the key components, following best practices, and staying aware of common challenges, you can develop a disaster recovery plan that keeps your business resilient in the face of unexpected disasters.
Remember, the goal of your IT Disaster Recovery Plan is to protect your business by minimizing downtime, safeguarding data, and ensuring a quick return to normal operations. With a well-thought-out plan in place, you can face the future with confidence, knowing that your business is prepared for whatever comes its way.